The Technology
Spondyloarthropathies (SpAs) are a family of inflammatory
processes associated with HLA B27 polymorphism that develop into a number of
conditions such as fusion of the spine or ankylosing spondylitis (AS), Reiter’s
syndrome (or reactive arthritis), psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s disease (a type
of IBD) and uveitis.
Our researchers believe that they have discovered
the mechanism of action for SpAs, based on shared homology of specific
peptide sequences that occur in Chlamydia trachomatis and also in a protein
called lumican which is preferentially and abundantly expressed in the locations
where SpAs manifest. The shared peptide sequences have very high binding
affinity to HLA B27, allowing the triggering of the immune response.
Investment Opportunity
NewSouth Innovations is looking for a partner to exclusively
license the technology and take on the clinical development of the diagnostic as
well as the potential vaccine specifically for SpAs.
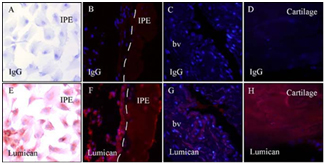
Lumican staining in human iris pigment epithelial
cells (IPE),
iris and synovial tissues. Human IPE cultures (A and E), iris
tissues (B and F), synovial tissues (C-D, G-H) were labelled
with
anti-lumican or control rabbit IgG, followed by HRP or
Alexa-fluor
conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG. Lumican staining
(red) is present in IPE in
vitro (E) and in vivo (F), in blood
vessels (bv) (G) and in articular
cartilage (H). Original
magnification x100 (A, E) and x400 (B-D,
F-H).
Please download the PDF of this Technology Brief